By: Adrian Lee, Sr Director Analyst
Erica Huang, Director Analyst
Gartner predicts by 2026, 30% of the organizations globally would have products and services ready for the metaverse, up from negligible levels now.
The metaverse is a persistent and immersive digital environment of independent, yet interconnected networks that will use yet-to-be determined protocols for communications. It enables persistent, decentralized, collaborative, interoperable digital content that intersects with the physical world’s real-time, spatially-oriented and indexed content.
Several companies, such as Meta Platforms (doing business as Meta and formerly known as Facebook), Microsoft, NVIDIA, Tencent and Roblox, have been envisioning and building their own versions of the metaverse. However, the enabling technologies are yet in emergent stages of evolution and limited to a niche, small segment of early adopters. Gartner expects metaverse will take more than eight years to reach early mainstream.
The solutions that are currently being positioned as metaverse are potentially compatible, but they do not meet the full definition of a metaverse. Early solutions may contain one or more attributes (persistence, decentralization, collaborativeness and interoperability) but not all of the attributes, which is required of a mature metaverse. Examples of early solutions include gaming, virtual collaboration, navigation apps, social media, and non-fungible tokens (NFTs). However, Gartner expects a mature metaverse will be device-independent and not owned by a single vendor: It will have a virtual economy of itself, enabled by digital currencies, NFTs or some equivalent (see Figure 1).
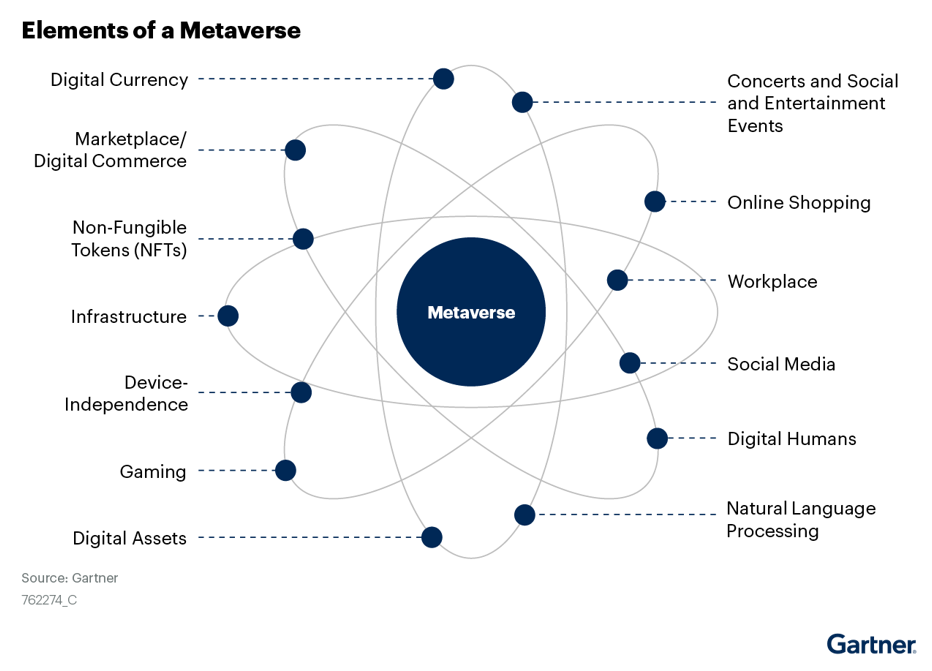
Figure 1: Elements of a Complete Metaverse
Initial Obstacles to the Success of the Metaverse
The road to build a mature metaverse solution may hit a number of challenges. If it remains fragmented and continues to provide siloed experiences, a complete metaverse will never be achievable. Furthermore, as each company tries to build its own fragmented version of the metaverse, it will only have a chaotic and an indiscernible structure that will lack combinatorial benefits. The following are some initial challenges that could hinder the development of a complete metaverse solution:
Governance is in very early stages of development, and there is a need to maintain a cohesive society as a basis for consensus governance that must be embedded while developing the metaverse. Otherwise, it could be detrimental to the society as a whole.
Security of the data would be a key concern and will need some fundamental regulations to protect the user information, as it will reflect the physical reality very closely. Investing in cybersecurity would be a key requirement to avoid deep fakes, hacked avatars, data breach and cyberattacks.
There could be tax and other regulatory issues once the digital commerce expands and represents an economy; even legal validity of businesses formed on metaverse will need to be decided going further.
There could be siloed development of each application for metaverse, which could result in a confounded world with multiple applications.
Lastly, organizational immaturity, in terms of building the products and services, may inhibit adoption.
Metaverse Is a Combinatorial Trend That Will Require Multiple Technologies and Trends to Form a Complete Metaverse
Currently, the innovators and early adopters of emergent metaverse solutions are providing device-dependent, siloed experiences. They have access-based delivery models, and all the products and services are designed around the models. The metaverse is still fragmented and indiscernible, since each enterprise is focusing on developing their own product independently.
The metaverse is a combinatorial trend in which a number of individually important, discrete and independently evolving trends and technologies interact with one another to give rise to another trend. It will require multiple technologies to create a parallel world augmenting physical and VR. The current solutions, like gaming, VR and navigation, use AR/VR, virtual assistants/NLP, IoT, multicloud, environmental mapping and biometric sensing to create the initial emerging metaverse solutions. The edge devices or smart devices are used to access these solutions. There are some technology consortia that may enable more viable Metaverse solutions, such as Oasis Consortium, or conferences like MetaCon, Metaverse Global Congress.
The advanced stage of metaverse is estimated to occur in 2023 or 2024. This will require AR cloud, spatial anchoring, sensor fusion, spatial orientation and indexing, multimodal UI, advanced virtual assistants, such as display independence, interoperability, data integration, 5G, distributed ledger, IoT, DNNs and AI applications. These are in addition to the one mentioned for the current solutions. Digital humans will play a key role, as they will need people to seamlessly move into skin (avatars) or own assets (for example, NFTs) across different applications. This stage is likely to continue for a longer period of time since, at this stage, there could be local government interventions, or the government may pose restrictions on the usage of some products/services that are related to privacy. An example includes the privacy concerns in Italy and Ireland over Facebook’s smart glasses. There could be more concerns as the advanced metaverse solutions come into existence. If organizations could come together, then a vendor-independent, interoperable and display-independent metaverse solution could finally come into existence by 2028.
As metaverse starts getting close to the point of maturity — at least seven to eight years from now, product leaders evaluating metaverse must include products and services in their future roadmaps. Major players like Meta, Microsoft and NVIDIA are already working on some initial solutions and are working on technologies to support the evolution, but some startups are also developing products and services in piecemeal fashion. However, in the near term, metaverse will be employed in limited areas. But in the future, the use of more sophisticated solutions, including more dynamic partnerships across the organizations developing it and more ecosystem partners, is expected.
Metaverse Will Displace Many Device-Dependent Interactions While Creating New Types of Interactions and Business Models Across Multiple Applications
While the benefits and opportunities from metaverse are not immediately viable yet, emerging metaverse solutions give an indication of potential use cases. We expect the transition toward metaverse to be as significant as the one from analog to digital. In physical world interactions, metaverse will supply real-time, interesting, actionable information across scenarios. Examples include wayfinding for both enterprise and consumer use, guidance for an industrial repair task, interactive demonstrations at a museum, dynamic information overlays for knowledge workers, and augmented social networking filters. In digital interactions, an example includes the ability to transverse different virtual realms. An example could include “teleporting” from an office meeting into a social gathering, into a video game or into an underwater tour — within any given interface/application. Although current metaverse experiences will not completely replace current digital interactions via apps, websites and so forth, it is likely to pave the way to new types of interactions and business models to optimize on these new use cases.
Metaverse will also have a wide-reaching and direct impact on multiple industries such as communications and media, retail, electronics, semiconductors, manufacturing, engineering, education, and banking. It will also have a direct impact on product and service marketing, branding, and sales roles in the organization, as metaverse is the next frontier for online interaction.
Areas adjacent to the product leaders’ current business provide rich opportunities for metaverse solutions because there may be new trends that develop as a result of combinatorial digital innovation. Current examples of “superapps” available, such as Grab or Meta, pack commerce, social media, private hire and online delivery business models in one single application, and provide a strong bellwether for the interoperability requirements for applications. As the metaverse reduces the dependence on users’ devices or applications, product leaders must look beyond the immediate contextual use of their products to identify opportunities that cut across applications.
Some industries, like gaming and navigation apps, will be early adopters. Some will soon progress to be included, such as social media, live concerts and events, virtual realty and workplaces. Product leaders need to closely track the success of use cases by each industry as they will signal their inclusion in the metaverse.

